Programming with Data Dependency Algebras (DDAs)
Data dependencies are inherent in the notion of an algorithm. Data dependency algebras (DDAs) [BH09] turn dependencies into explicit, programmable entities, that are more fundamental than general dependency analysis of, e.g., loops in an imperative program. DDAs abstract how parts of a computation depend on data supplied by other parts at a fine-grained level.

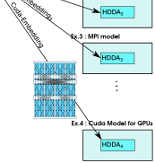
A hardware architecture’s space-time communication layout can be defined as a special Hardware Space-Time DDA. It has projections into space and time, where space comprises the hardware’s static spatial connectivity pattern. By embedding a computation’s DDA into the Space-Time DDA of the hardware, we map the computation onto the communication layout of the hardware.

In a DDA-enabled compiler each hardware system is associated with a computational mechanism based on its Space-Time DDA. The generated code has precise placement of the computation steps as defined by the embedding. We are developing the Magnolia language to support DDA-based programming.
Portability: In the figure, DDA + Expression is hardware independent. Embeddings onto various hardware is defined from the DDA, and is thus reusable when the DDA is reused.
Reusability: The Butterfly pattern, used as an example here, appears in many divide & conquer algorithms, sorting networks and signal processing problems. The same DDA and embeddings can be reused for many computations, only the expressions differ.
Embeddings are high-level and controlled by DDA projections, usually short, reusable code snippets. The extra detail in the example shows the Bitonic Sort DDA embedding onto CUDA.
Our current DDA project is a continuation of a previous project, where the simple DDA-based language Sapphire was developed. Some more examples are available on the old project pages.
People and Partners
Staff
- Prof. Magne Haveraaen, project leader
- Dr Eva Burrows, postdoc
Related People
- Steinar Søreide – worked on the DDA-based Sapphire language
References
- [BH12]
- Eva Burrows and Magne Haveraaen. Programmable data dependencies and placements. In Proceedings of the 7th workshop on Declarative aspects and applications of multicore programming, DAMP '12, pages 31-40, New York, NY, USA, 2012. ACM. [ bib | DOI ]
- [Bur11]
- Eva Burrows. Programming with Explicit Dependencies: A Framework for Portable Parallel Programming. PhD thesis, Research School in Information and Communication Technology, Department of Informatics, University of Bergen, Norway, PB 7803, 5020 Bergen, Norway, 2011. [ bib | .html | .pdf ]
- [BH09]
- Eva Burrows and Magne Haveraaen. A hardware independent parallel programming model. Journal of Logic and Algebraic Programming, 78:519-538, 2009. [ bib | DOI ]
- [CH95]
- Vytautas Čyras and Magne Haveraaen. Modular programming of recurrencies: a Comparison of Two Approaches. Informatica, 6(4)397-444, 1995. [ pdf ]
- [Hav00]
- Magne Haveraaen: Efficient Parallelisation of Recursive Problems Using Constructive Recursion. In Arndt Bode and Thomas Ludwig and Roland Wismüller (editors): Euro-Par 2000, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, volume 1900, pp. 758--761, Springer Verlag, 2000. [ DOI ]
- [HS98]
- Magne Haveraaen and Steinar Søreide. Solving recursive problems in linear time using Constructive Recursion. Proceedings of Norsk Informatikk Konferanse NIK'98, Tapir, Norway, 1998, pp. 310-321. [ ps ]
